Dear Editor,
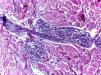
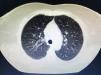
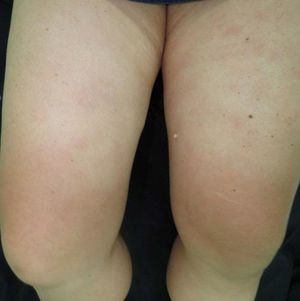
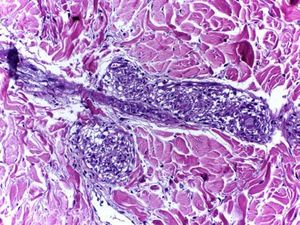
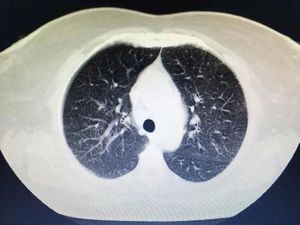
Sarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory disease of unknown etiology that manifests as noncaseating granulomas. Skin involvement is frequent, occurring in 25–35% of cases.1 We report a case of sarcoidosis manifested as livedo on the lower limbs, which is an atypical and rare presentation. A 52-year-old woman presented with fatigue, intermittent low fever, and erythematous patches on both legs, followed by a local burning sensation for over a month. She reported a prior history of arthralgia of the hands and knees for 4 years. Skin examination showed erythematous-violaceous livedoid macules symmetrically distributed on the anterior and medial surface of the thighs and knees (Figure 1). Histopathological examination of the livedo area showed uniform sarcoid granulomas composed of histiocytes with large and eosinophilic cytoplasm, vesicular oval nucleus, and prominent nucleolus, in association with Langhans giant cells. The periphery of the granulomas showed scarce lymphocyte infiltrate (naked granuloma). The connective tissue was normal with absent vasculitis (Figure 2). Due to clinical and histopathological findings, the diagnosis of cutaneous sarcoidosis was established. Laboratory results revealed microcytic and hypo-chromic anemia with hemoglobin level of 10.5 g/dL, erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 20mm/h, and angiotensin-converting enzyme level of 107 U/L (20–70 U/L). Results for p-ANCA and c-AN-CA were both negative. Chest computed tomography revealed diffuse bilateral distribution of multiple centrilobular nodules and bronchial wall thickness (Figure 3). Abdominal ultrasound showed calcifications in the right lobe of the liver. An elective laparoscopy to fix a hiatal hernia showed several nodules on the liver surface, which were described as sarcoid granulomas on histopathological analysis. The patient remains in periodic consultation and showed partial improvement of the systemic manifestations and full resolution of the livedo on prednisone 20mg/day. Sarcoidosis is a systemic granulomatous disease whose cutaneous manifestations are extremely polymorphic. Skin lesions may be classified, according to the histological differences, as specific - which histopathology reveals typical sarcoid granuloma, corresponding to 90% of the cases - or nonspecific.2 Although the classic specific cutaneous manifestations are erythematous-violaceous or yellow-brown nodules and plaques, other forms have been described, such as maculopapular lesions, annular lesions, atrophic lesions, hypochromic macules, painless subcutaneous nodules, alopecia, erythroderma, ichthyosis, psoriasiform lesions, lichenoid lesions, and warty lesions. Livedo is not mentioned as a cutaneous manifestation in sarcoidosis by most authors. In these cases, most patients are young female adults, with lesions located on the lower limbs, similar to our case.3 Shibama et al. (2014) reported a case of cutaneous sarcoidosis in a 57-year-old Japanese woman who complained of reddish lesions on the legs. Histopathological examination of the subcutaneous nodules in the livedo area showed noncaseating epithelial granulomas disseminated through the dermis, lower dermis, and the hypodermis.4 In other diseases, livedo is classically caused by hypoxia and low perfusion at the peripheral skin, usually related to an injury to the blood vessel wall or to obstruction of its lumen, which leads to an interruption of blood flow in that area. In sarcoidosis, this phenomenon can be attributed to a disturbance of microcirculation caused by the infiltration of sarcoid granulomas, leading to intraluminal abnormalities and extrinsic compression, without vasculitis. Histopathological examination is crucial for the exclusion of other etiologies, such as peripheral atherosclerosis, thrombosis, connective tissue diseases, and other autoimmune diseases with vasculitis.3,5 The cutaneous presentation of livedo is also associated with the presence of granulomas in other organs. Therefore, multisystem screening should be performed.3 Because no lesion is pathognomonic of sarcoidosis, the diagnosis is made by excluding other similar diagnosis. On clinical suspicion, the supplementary assessment must include blood count, assessment of kidney function, urinalysis, and electrocardiogram. Hypercalcemia, calciuria, and increased levels of angiotensin-converting enzyme may be found among the results. Chest X-ray or CT must also be requested. Depending on the severity of the disease, with skin and other systems involved, glucocorticoid therapy may be efficient and should be the first choice.1 Although livedo in sarcoidosis has spontaneous remission most of the times, in severe cases,oral glucocorticoids may be necessary to control the symptoms.3-5 The present report illustrates a case of livedo caused by extrinsic obliteration and intraluminal changes of the blood vessels due to the presence of noncaseating granulomas in the absence of vasculitis. This is a very rare cutaneous manifestation, not usually mentioned as a specific manifestation of sarcoidosis, with only a few cases reported in the literature.
Sarcoid granulomas composed of histiocytes with large and eosinophilic cytoplasm, vesicular oval nucleus and prominent nucleolus, in association with Langhans giant cells. The periphery of the granulomas showed scarce lymphocyte infiltrate (naked granuloma). Vasculitis was absent (Hematoxylin and eosin, x100)