Dear Editor,
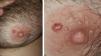
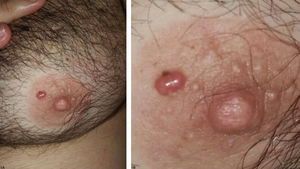
We report a case of a 36-year-old male patient with a two-month history of an asymptomatic, erythematous, 1 x 1cm papule of fibroelastic consistency on the left areola (Figure 1). The left axillary lymph nodes were not enlarged.
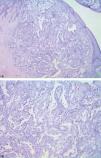
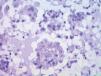
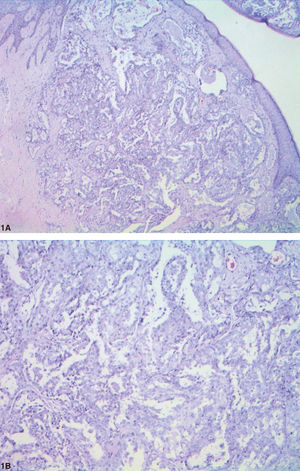
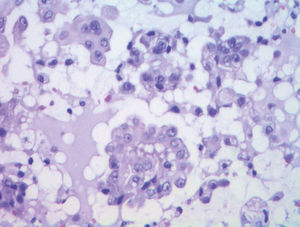
We performed an excisional biopsy of the papule for diagnosis. Histopathology revealed a dermal tumor with no connection to the overlying epidermis. The lesion contained cells with papillary folds, tubules, cystically dilated spaces, and lumen lined by columnar cells with decapitation secretion, compatible with hidradenoma papilliferum (HP) (Figures 2 and Figures 3).
HP is a rare, benign, adnexal tumor that occurs almost exclusively in the anogenital region of female patients.1-4 HP appears as solitary, asymptomatic, well-circumscribed, skin-colored or reddish-brown nodules measuring from 0.5 to 1cm. HP lesions that are not located in the anogenital area are referred to as ectopic HP.1,4,5
Many cases of HP have been reported since it was first described by Werth in 1878.5 However, very few cases of ectopic HP have been reported in male patients.4 Ectopic HP can occur on the eyelids, orbit, nose, breast, chest, abdomen, and scalp.4,5
The histogenesis for both anogenital and ectopic HP remains unclear. Although the presence of human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA has been identified in a few cases, it does not seem to play a role in the pathogenesis of HP. Histopathological findings show dermal tumors with no connection to the overlying epidermis, with papillary and tubular formations, cystically dilated spaces, and lumen lined by columnar cells with decapitation secretion. Such histopathology findings are similar to those observed in intraductal papilloma of the breast and some authors believe that accessory mammary-like glands may have a role in the histogenesis of the tumor.5
The actual incidence and prevalence of ectopic HP is unknown due to the low number of cases reported. Kim et al. compiled the clinical data available from all 19 patients previously reported. Despite the small sample, some aspects are wotth mentioning. The mean age of patients with ectopic HP ranged from 40 to 59 years (10 to 20 years more than the mean age for patients with anogenital HP). In contrast to anogenital HP, nearly one half of the patients with ectopic HP are men and lesions are located mainly on the head and neck.4
Histological examination is required for the accurate diagnosis of HP.5 The differential diagnosis for ectopic HP includes benign adnexal tumors, such as apocrine hidrocystoma and syringocystadenoma papilliferum.5 In our case, we included clinical differential diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma, epidermal cyst, and pyogenic granuloma.
Malignant transformation is very rare. Five cases of ductal carcinoma in situ arising within a pre-existing hidradenoma papilliferum have been documented, and two cases have reported invasive carcinomas arising from HP (malignant perianal papillary hidradenoma and vulvar adenosquamous carcinoma).5
The treatment of choice for ectopic HP is complete excision of the tumor,4 as in the present case, and recurrence is typically attributed to incomplete excision. 1,4
Financial support: None.
Conflict of interests: None.